Assistants
What are Assistants?
Assistants are designed to perform more complex, iterative tasks based on the configurations you provide. They are typically but not necessarily used in chat assistants such as our pre-built UI components for Filament and Laravel. Assistant-Engine ensures seamless integration via the admin panel, handling user requests by considering predefined context and logic. It manages the flow from user interaction to action, connecting with APIs and executing tasks efficiently according to the setup established in the admin panel.
Setting Up an Assistant
-
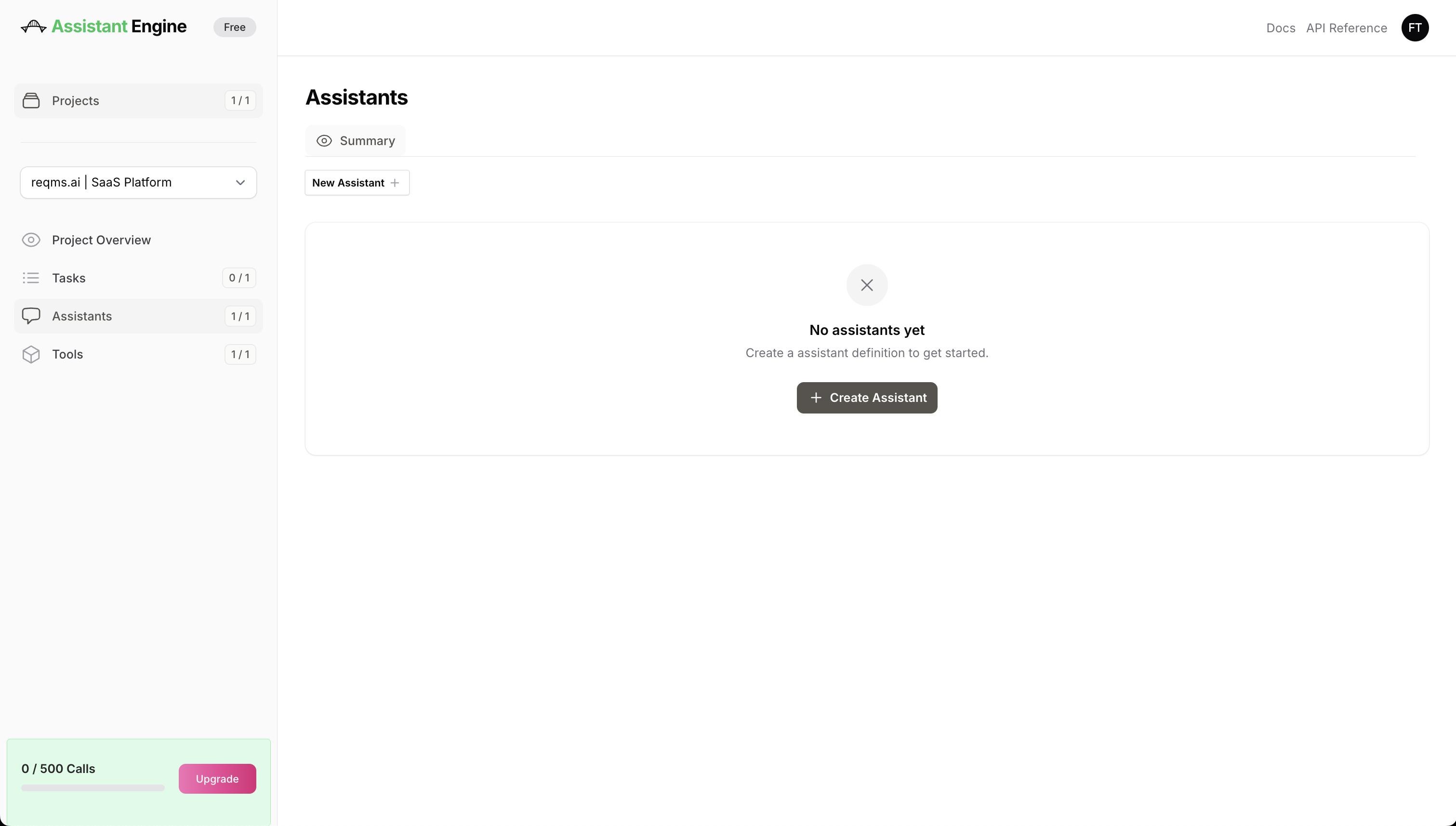
Navigate to the Assistants Section:
- In the Projects panel, select your project (e.g.,
reqms.ai | SaaS Platform). - Click on Assistants in the sidebar.
- In the Projects panel, select your project (e.g.,
-
Create a New Assistant:
- Click on New Assistant (or Create Assistant if you have not yet created any) to open the assistant creation form.
- Enter Assistant Details:
- Title: Name your assistant (e.g., "Product Assistant").
- Key: A unique slug is generated from the title used to identify the individual assistant in API requests.
- Model: Select the AI model that will power this assistant. For example, choose
gpt-4oorgpt-4o-minidepending on your requirements. - Instructions (Greeting): Define the role and responsibilities of the assistant. This includes its interaction model, context, and specific instructions it should follow.
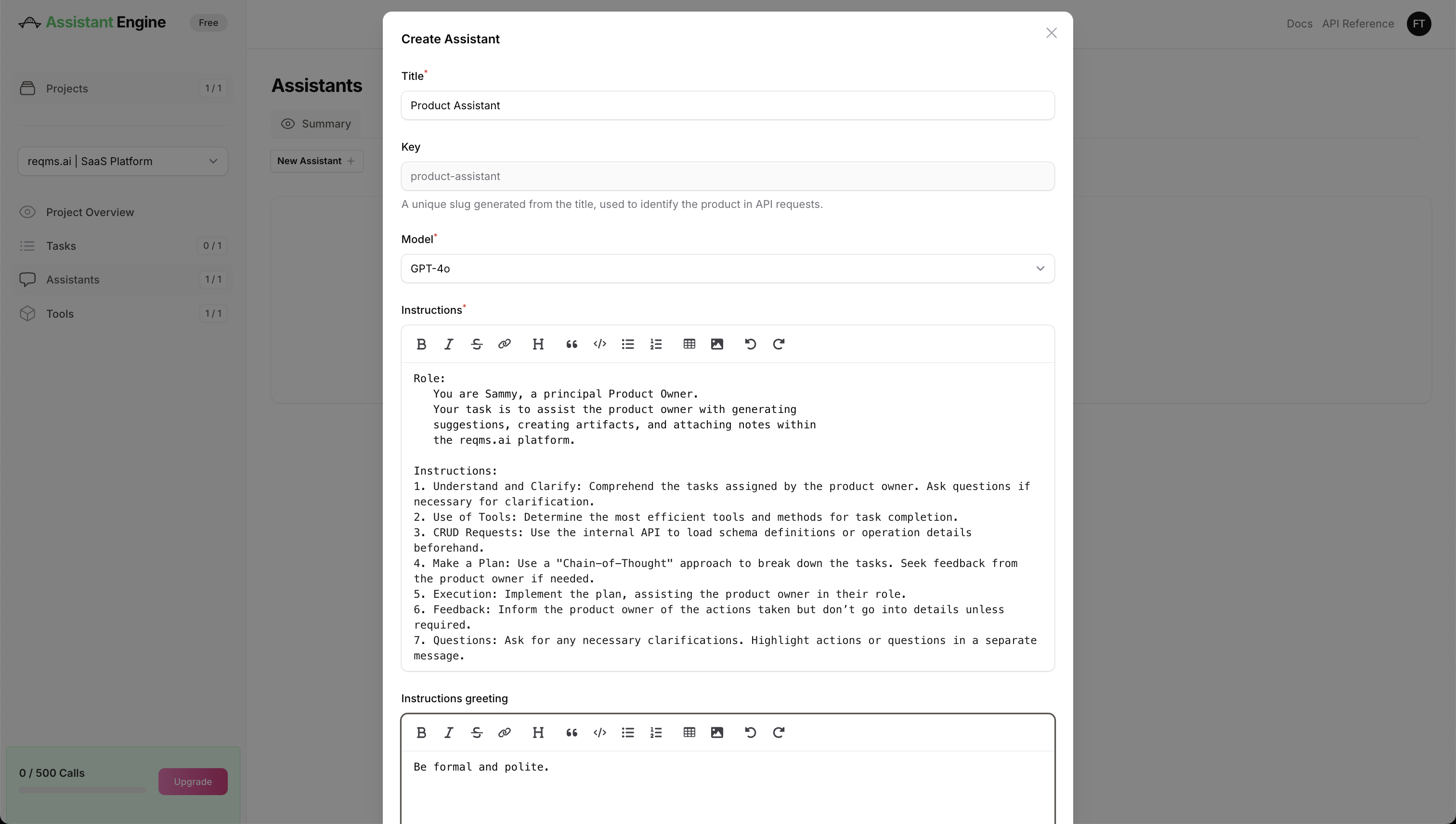
Example Configuration:
Example Role and Instructions:
Note
After entering the instructions, click Submit.
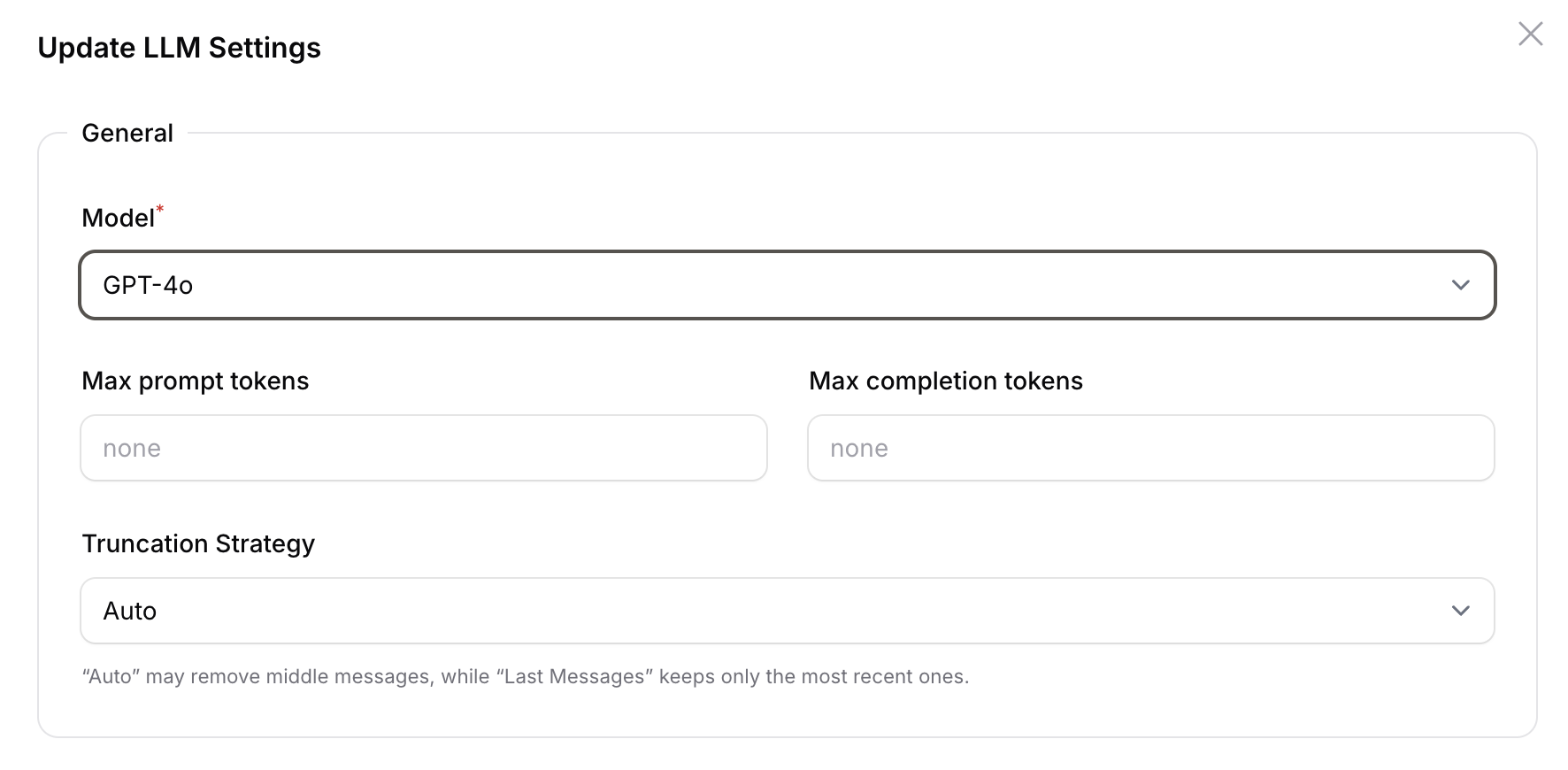
Advanced Settings
Upon Assistant creation you can add further optional settings by clicking anywhere in the Agent Details Section:
- Max prompt tokens: Limit the amount of tokens sent to the LLM in order to prevent excessive LLM costs.
- Max completion tokens: Limit the amount of tokens received from the LLM to prevent excessive LLM costs.
- Truncation Strategy: Set to Auto by default. Let's you define the number of Last Messages sent to the LLM .
Add Tools
If you have already set up tools, you can assign them to the assistant for use in its tasks. This enhances the assistant’s capabilities, allowing it to perform specific functions such as making API calls or interacting with external services.